In cleanroom environments, such as those found in semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, precision electronics, and biotechnology, the wheels of mobile equipment are often overlooked yet critical components. Choosing the wrong material can lead to the generation of particulates, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or electrostatic discharge (ESD) during friction. These factors can directly cause a drop in product yield or lead to production line contamination.
1. Core Performance Requirements
Materials used in cleanroom environments must meet three hard indicators:
Low Particulate Generation (Low Outgassing & Shedding): Materials must not peel or generate dust, even under frequent steering and friction.
Chemical Resistance: Cleanroom floors are often treated with aggressive disinfectants or cleaning agents; therefore, materials must be corrosion-resistant.
Non-Marking: Wheels must prevent leaving skid marks or streaks on expensive epoxy or PVC flooring.
2. In-Depth Analysis of Mainstream Materials
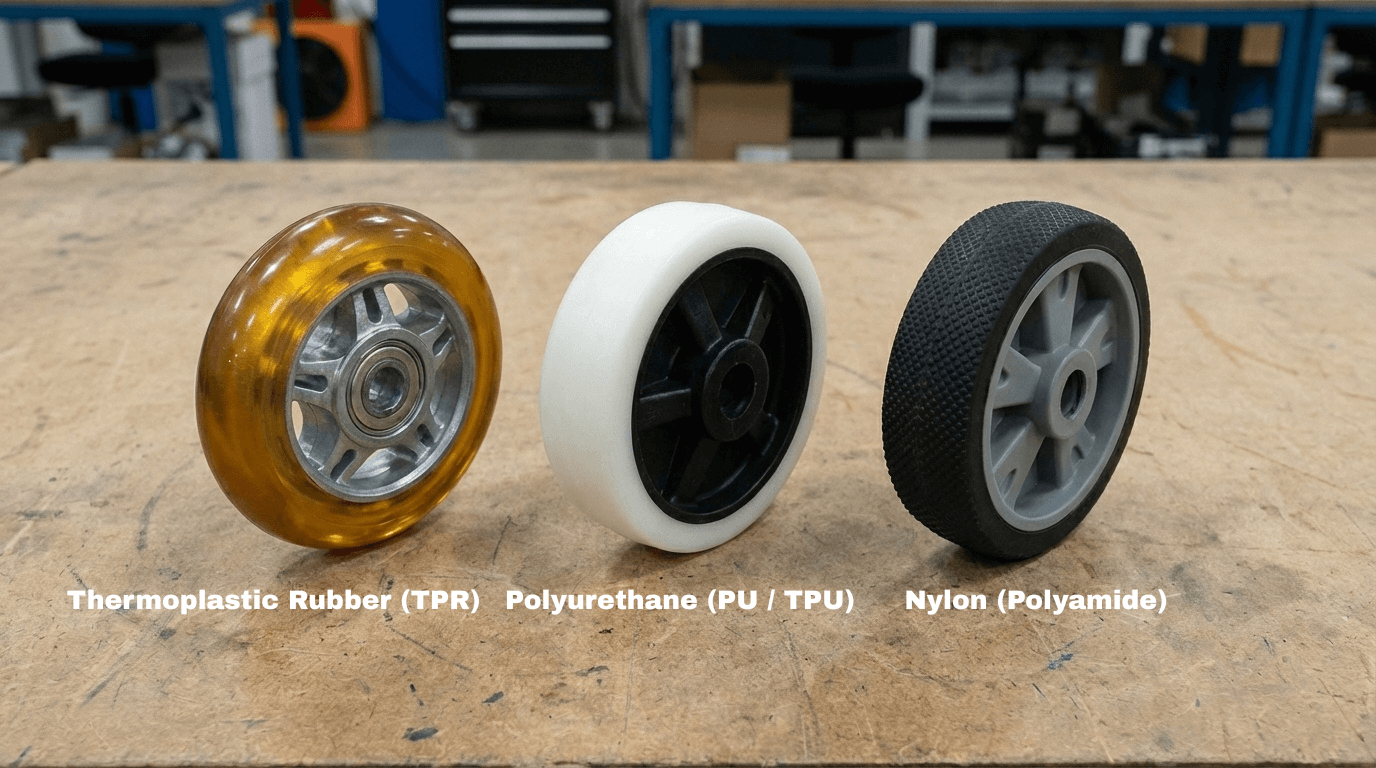
Polyurethane (PU / TPU)
This is the most common material used in cleanrooms, especially high-purity Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU).
Advantages: Excellent wear resistance, high load capacity, and low operational noise. High-quality PU does not become brittle or age as easily as standard rubber.
Applications: Pushcarts, mobile workstations, and medium-duty equipment.
Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon is a hard material with extremely low rolling resistance.
Advantages: Virtually no particulate shedding, highly resistant to chemical corrosion, and suitable for heavy loads.
Disadvantages: Due to its hardness, if small particles are present on the floor, nylon wheels may crush them or potentially damage the floor surface.
Applications: Transporting heavy precision instruments and heavy equipment in fixed long-term positions.
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR)
TPR combines the softness of rubber with the cleanliness of plastic.
Advantages: Superior shock absorption, making it ideal for protecting fragile wafers or optical lenses.
Caution: It is essential to ensure that "Cleanroom Grade" TPR is used to prevent the outgassing of plasticizers, which causes molecular contamination.
3. Anti-Static and Conductivity (ESD & Conductive)
In a cleanroom, static electricity not only attracts dust but can also puncture and destroy sensitive electronic components.
ESD Wheels: Surface resistance typically ranges between 10^6 Ω and $10^9 Ω.
Conductive Wheels: Lower resistance, typically less than 10^6 Ω.
Material Implementation: Usually achieved by adding Carbon Black or modern conductive polymers to the polyurethane or nylon, allowing static to dissipate through the wheel into the conductive flooring.
4. Hardware Integration: Rigs and Bearings
Material selection is not limited to the wheel tread; the housing and bearings must also meet cleanroom standards:
Stainless Steel (304/316): The only choice for rigs/brackets to prevent rust and metallic debris.
Sealed Bearings: Prevents internal grease leakage and stops external contaminants from entering the bearing race.
Full Synthetic Grease: Uses specialized low-volatility, low-diffusion cleanroom lubricants.
5. Summary and Recommendations
Material | Load Capacity | Shock Absorption | Cleanliness Class (Ref) |
Polyurethane (PU) | High | Excellent | ISO Class 3-5 |
Nylon | Extra High | Poor | ISO Class 1-3 |
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Medium | Superior | ISO Class 5-7 |
Are you looking for replacement parts for specific cleanroom equipment? If so, please contact us, and we will tailor a solution for your needs.





